
Upon its launch in November 2022, ChatGPT, the generative text platform developed by OpenAI, garnered immediate public acceptance. Within two months, the platform amassed a user base of 100 million individuals. Users quickly identified many use cases for ChatGPT outputs, leading to widespread reliance on the platform across various technologies.
As millions of users continued inputting into the ChatGPT chatbot, unforeseen problems emerged. At Samsung, multiple employees inadvertently shared sensitive internal source code and proprietary data through ChatGPT. While these Samsung users wanted to use ChatGPT to solve problems and simplify their lives, they were leaking data to a third party instead.
As this data leak came out, it sent a shock rippling through all ChatGPT users. The terms “public AI” and “private AI,” previously not part of the conversation, were suddenly thrust into the spotlight. Users and businesses already integrating generative AI tools into their workflows had to stop and understand the differences between public and private AI and how to pick the right type for their AI use case.
Defining Private AI and Public AI
Although there isn’t a definitive “right” or “wrong” AI type, the suitability depends on your specific use case. As a business owner, weighing the advantages and disadvantages of both public and private AI before implementing it within your business is crucial.
Private AI
Private AI refers to artificial intelligence systems operating in closed, restricted environments often trained on proprietary data. These systems are typically owned and controlled by specific entities who want to manage the data feeding the system and retain the IP of the models involved.
The primary characteristic of private AI lies in its exclusivity. These systems limit access, only allowing authorized personnel or entities. They are suitable for processing sensitive data and proprietary information, keeping the system closed with heightened security measures to safeguard against unauthorized access.
In private AI settings, the focus is on tailoring AI applications to the specific needs and objectives of the owning entity. This customization allows for developing specialized algorithms and models optimized for the unique challenges and opportunities within the closed environment.
In industries like healthcare and finance, Private AI plays a crucial role in providing personalized services and maintaining confidentiality, underscoring its significance in sectors where privacy, compliance, and customization are paramount.
Summary of Private AI
- Private AI operates in closed, restricted environments.
- Access to private AI systems is limited to authorized personnel or entities.
- Private AI often focuses on customization for the specific needs and objectives of the owning entity.
Public AI
Public AI is characterized by accessibility to a broad audience. They are systems developed and deployed to be widely available to the public or specific user groups.
Public AI applications can be accessed through open platforms, APIs, or cloud-based services. These access points allow users to leverage AI capabilities without needing the extensive infrastructure or expertise to run private AI platforms.
Public AI is a more democratized approach to artificial intelligence. Its platforms aim to make artificial intelligence technologies more accessible, inclusive, and available to a broader range of people.
Public AI can include machine learning libraries, pre-trained models, and cloud-based AI services provided by tech giants. The inherent access to public AI encourages developers to be creative with the technology and businesses to use AI for various applications, from natural language processing to image recognition.
Summary of Public AI
- Accessibility to a broad audience.
- Accessible through open platforms, APIs, or cloud-based services.
- Democratized approach to AI, aimed for multiple usages.
- Includes machine learning libraries, pre-trained models, and cloud-based services
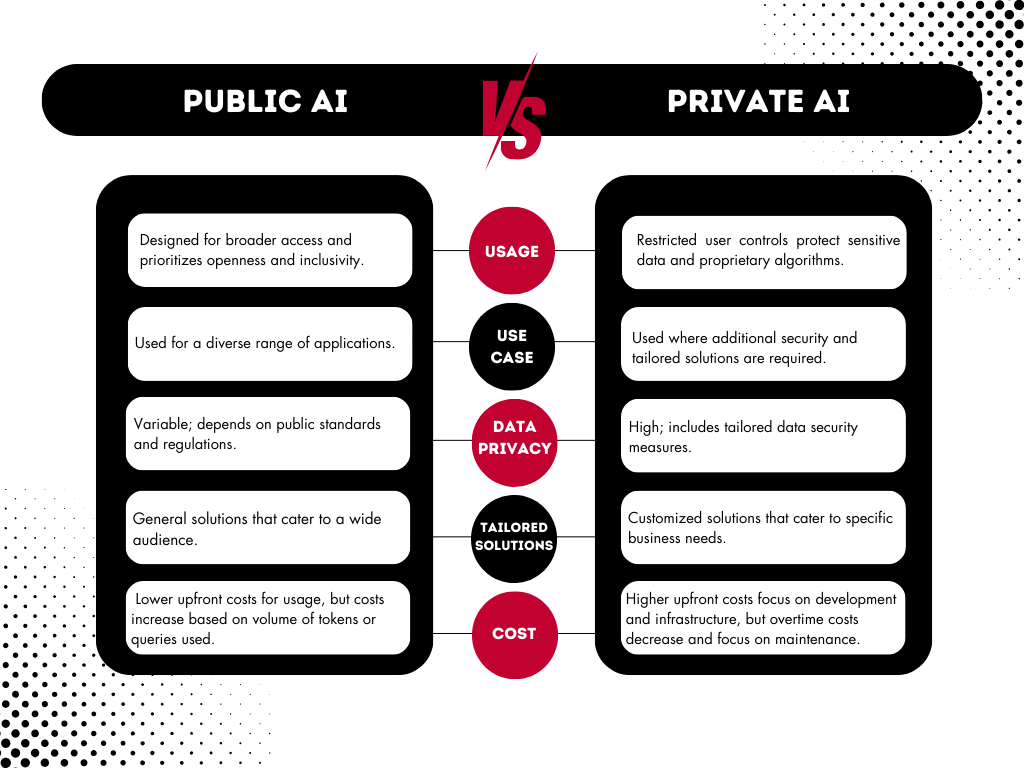
5 Key Differences of Public and Private AI
If you’re contemplating AI implementation or your business already leverages AI – make sure you know the distinction between public and private AI. Understanding these differences will ensure you choose the right AI solutions for your business and avoid any potential pitfalls or data leak incidents.
Usage
Usage refers to the mechanisms and policies to manage and regulate the usage of AI systems.
- Private AI: Restricted usage is a defining characteristic of private AI, with stringent usage controls to protect sensitive data and proprietary algorithms.
- Public AI: Designed for broader access, public AI prioritizes openness and inclusivity, enabling a wide range of users to benefit from AI capabilities.
Use Case
Use cases highlight the practical applications and scenarios where AI technologies are deployed to address specific challenges or optimize processes.
- Private AI: Commonly applied in settings where specialized, tailored solutions are required, such as optimizing internal business processes or conducting proprietary research.
- Public AI: Widely used for diverse applications, ranging from consumer-facing AI features in mobile apps to large-scale data analysis and research projects.
Data Privacy
Know the risks and vulnerabilities associated with using and deploying artificial intelligence systems. This includes data breaches, unauthorized access, and privacy violations.
- Private AI: High security measures to protect against unauthorized access and potential breaches.
- Public AI: Variable security measures, as public AI depends on public standards and current regulation.
Tailored Solutions
Refers to who decides how the AI applications are used and developed. This can either be controlled by specific groups or spread out among different communities or organizations.
- Private AI: Owned and controlled by specific entities, private AI allows for AI applications to be customized to meet specific business needs.
- Public AI: Operates in a more decentralized manner, public AI offers general solutions that cater to a wider audience.
Cost
Cost considerations differ between public and private AI due to their distinct ownership and control structures.
- Private AI: Because private AI is owned and controlled by specific entities, the costs typically revolve around the investments required for development, maintenance, and infrastructure.
- Public AI: The costs associated with public AI vary but could be extremely cost-prohibited the more data you need. While public AI platforms may offer more accessible entry points and reduced infrastructure requirements for users, there may still be costs involved in using large amounts of data or accessing advanced functionalities.
Navigating the Landscape: Striking a Balance
The choice between private AI and public AI is often a strategic decision influenced by various business factors, including the nature of the application, data sensitivity, organizational objectives, and compliance guidelines.
In scenarios where data privacy and control are paramount, private AI offers a tailored solution. Organizations can develop and deploy AI applications that align precisely with their needs, ensuring the confidentiality of proprietary information.
As industries recognize the potential for collaborative advancements, efforts to bridge the gap between private and public AI will gain momentum. Open-source initiatives, industry collaborations, and ethical AI frameworks will contribute to a more inclusive and responsible AI ecosystem.
At Rōnin Consulting, we are developing an AI platform called SamurAI that will enable organizations to utilize multiple AI models, both private and public, allowing the capture of important AI audit information and enforcement of compliance controls to align with the business’s needs. This platform simplifies integrations with existing business systems and allows real-time monitoring of the models. To learn more about public AI and private AI, or how SamurAI could work for your business, reach out to us today.
Want More Content Like This?
Join the Rōnin Recap
Get expert insights on AI, integration, and the future of software — direct from the team at Rōnin Consulting. We’ll send you the good stuff, not spam.





